Shading devices
The studio offers a consulting services and professional assistance to designers, manager, clients to choice the right strategies to reduce the energy requirements for summer air conditioning of buildings through the evaluation and analysis of different shading devices.
The control of the incident solar radiation is a important aspect in a well planning to minimize the energy consumption of buildings.
The reduction of energy requirements for summer air conditioning can be achieved through different design strategies as glass use with certain characteristics and shading devices.
In general, a glass with low levels of visible transmittance τv and solar factor gv can help to reduce the cooling loads limiting the requirement, however, reducing solar heat gains cause in winter a higher heating demand. In nearly zero energy building this parameter influence the global energy balance.
To prevent summer overheating and glare directed a good design strategy should be used glazed openings in conjunction with to shading devices. Installation of external movable sun shading devices is highly recommended in glazed openings that are exposed to the summer sun. Well designed sun shading devices will help keep the building cool and comfortable and limit the space conditioning needs. Living comfort means increase:
- thermal comfort: the control of indoor space factors (relative humidity, operating temperature, ...) values allows a drastic reduction of energy cooling consumption
- visual well being: control of lighting levels
- acoustic comfort
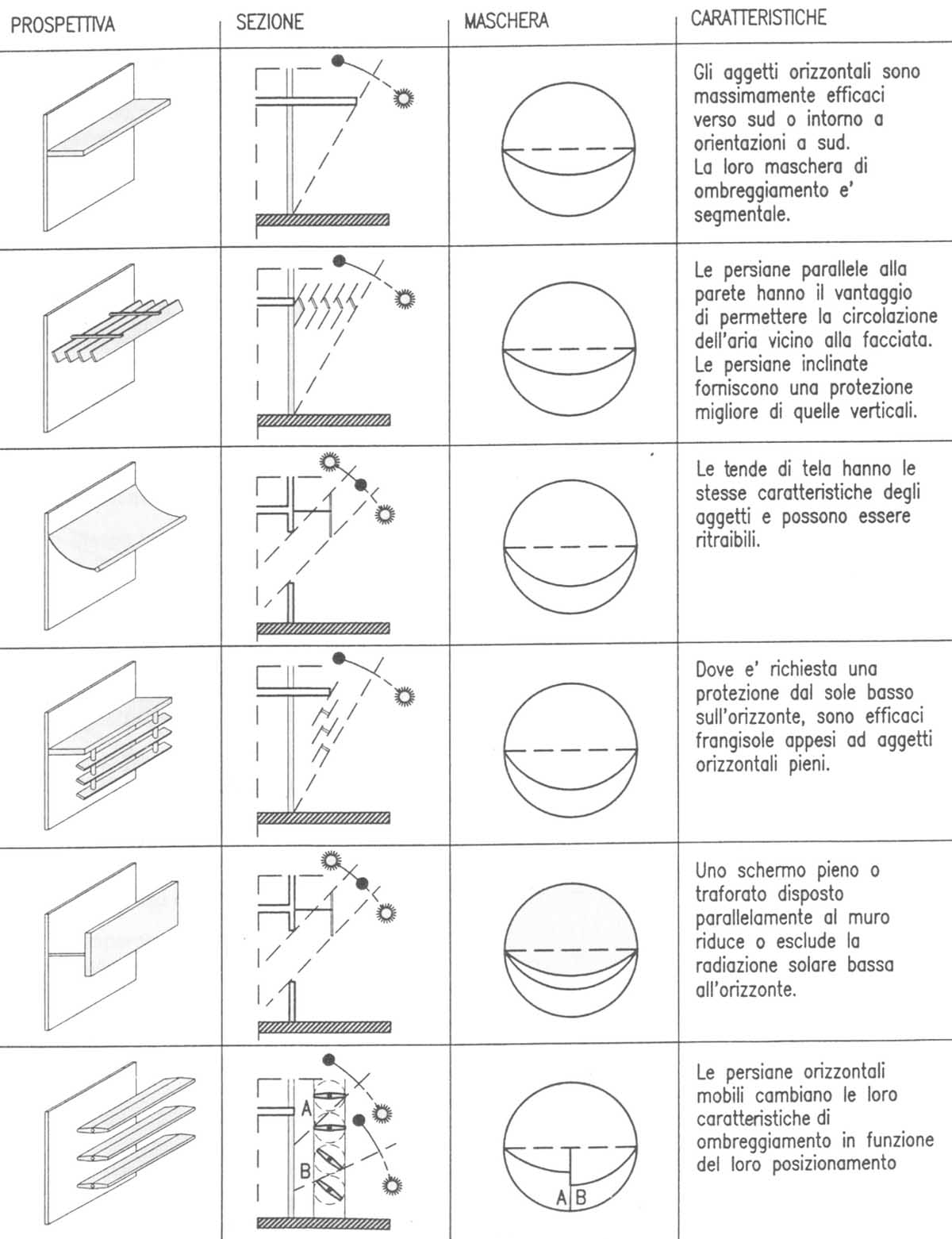
The shading devices are generally classified according to their position relative to the frame in:
- external shading devices
- louvres system (fixed/ movable) parallel/ orthogonal to the façade with horizontally or vertically plane;
- adjustable persian shutter (blinds, sliding, …);
- external venetian;
- tents (a different movement system
- internal shading devices
- adjustable persian shutter
- internal venetian;
- tents (a different movement system)
- integrated shading devices
The shading devices are often distinct from their geometry in horizontal and vertical and from type of installation in fixed and movable. Some examples of horizontal and vertical shading devices are showed.
Efficiency of shading devices
The correct evaluation of performance of energy efficient shading devices has the following purposes:
reduce unwelcome solar gains:
the incident solar radiation pass through the trasparent components is intercepted by the shading device which in the case of external installation offer the best performance to reduce indoor temperature;reduce cooling loads in summer:
summer season reduction of solar heat gains allows to minimize the energy demand necessary for the cooling of the indoor space;reduce electricity consumption:
reduces the heat generated by the lamps and consequently the energy loads for air conditioning;lighting control:
uniform distribution of luminance influence visual comfort because you can avoid the problem due to the excessive brightness at the windows and dim light in the inner areas. Some shading devices allow to create right level of illumination for specific work conditions;provide good quality lighting without glare:
in winter when the sun is low on the horizon may create some problem of glare can be eliminated by shading devices;external vision:
shading devices in addition to offering a solar protection can satisfy the physiological users need to be able to see outside;use of space indoor / outdoor:
often can happen, especially in the summer, that interior or external spaces, such as hallways, balconies, terraces, squares become inaccessible at certain times of day because solar irradiation is too high. The shading devices are used to create comfortable shading areas;UV protection:
buildings as museums, exhibition spaces, libraries requires protection from direct solar radiation. Shading devices use is an excellent design solution;architectural language:
thanks to development of the industry the designer has a lot of opportunities to create new composition of buildings facades
On the intervent of a building refurbishment several studies have been conducted on how combined solutions to reduce energy cooling demand.
To prevent overheating in summer has been taken the solution to install external shading devices. Different type of shading devices have been assessed through dynamic simulations of thermal behavior indoor space.
An example of some results of the different solar shading devices assessment are reported for a summer on 15 July considering climatic conditions of Florence city. Indoor cooling setpoint temperature at Ti = 26 ° C and occupacy from Monday-Friday during the hours 8:00 to 18:00, air conditioning with mechanical ventilation system. For internal gains for internal contributions have been used 10 W/m 2 for offices, 30 W/m 2 for meeting rooms.





