Airtightness

As show the graph thermal insulation and ventilation parameters significantly influence energy balance of a conventional building.
Both are directly connected to the airtightness of the building envelope. Airtightness is an important requirement for improve energy efficient building and avoid moist room air penetrate into the construction, condense and cause damage: air tight design is important to keep pleasantly warm the inner surfaces, maintain a comfortable and healthy interior environment.
Low level of airtightness can determine:
- increased heat losses and greater heating/cooling demand
- risk of condensation
- reduced levels of comfort indoor. Draughts resulting from gaps in the facade are responsible of cool inner surfaces (local discomfort) and uncontrolled humidity inside the building.
- reduced acoustics insulation
- reduced efficiency of the heat recovery ventilation systems because warm air pass through gaps of building can not recovery
The key to reducing air infiltration through building is design continuous uninterrupted airtight building envelope. The airtightness it consists of one uninterrupted airtight envelope layers enclosing the whole heated space able to prevent air flows pass from inside to outside. Outer layer can be used to limit the passage of wind and protect the structure on the outer side against the entrance of cold drafts in winter or hot summer.
Airtightness layer is generally placed on the inner side of the insulating layer and can be used as vapour barrier.
The level of building airtightness is measured through the Blower Door Test which allows to evaluate the permeability of the envelope by calculation of infiltration rate at 50 Pa, a pressure difference between inside and outside (the pressure test generated corresponds approximately to a dynamic pressure generated perpendicular on a wall subject from the wind at 9 m/s speed.
Test is performed by using a variable-speed fan mounts into the frame of an exterior door or window (all other openings are closed) which pulls air out of the house, lowering the air pressure inside in order to create difference of 50 Pa pressure. Pressure gauge connected to the fan measure the airflow rate per minute required to keep heated space at a constant pressure. According to EN13829 standard the test does consist of a multi point reading are taken at different pressure points of underpressure or overpressure of no more than 10 Pa differences and the information gathering compares with estimated values based on the volume of the house. The presence of leaks can be identify by anemometer or a smoke pencil.
Passivhaus standard requires both directions to be tested, with the result being an average of the two. To meet the passive House criteria, the tested building must have an air change rate of 0,6 h-1 (or ach) at 50 Pa:
n50 = V50 / V [h-1]
n50 = is the air leakage rate at a pressure difference of 50 Pa
V50 = is air flow rate measured [m3 /h]
V = is the volume of air inside the building under test, for all the zones incorporated within the test zone [m3]
Italian building legislation does not impose any requirements about air permeability of building envelope in new dwellings or refurbishment. However, there are various municipalities and provinces have adopted in their local legislation a certification process which requiring limit values of air exchange n50 certified through the Blower Door Test.
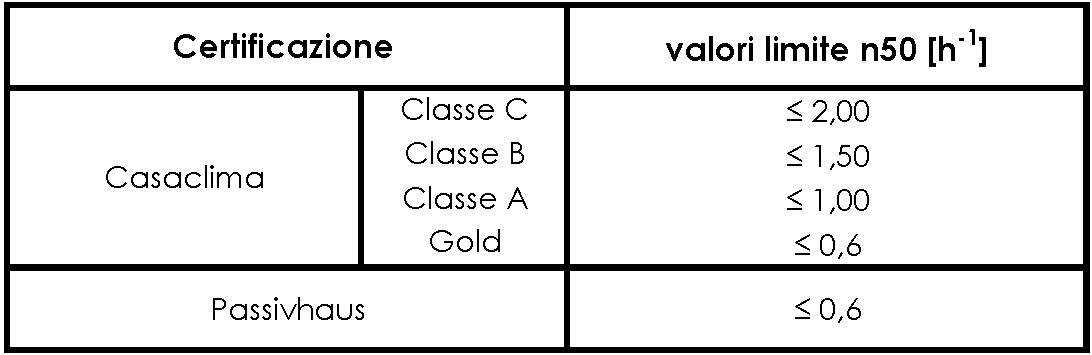
The certification process Casaclima Agency of Bolzano fixed for all residential buildings of new construction a limit value n 50 according to the energy class.
House built according the standard passivhaus the infiltration rate at 50 Pa overpressure is set to 0.6 ≤ h-1.
The EN13829 standard lists two principal test preparation methods, which are given as Method A and Method B:
Metodo A(test of a building in use): the condition of the building envelope should represent its condition during the season in which heating or cooling systems are used. This method is used to determine the value n50 .
Metodo B (test of the building envelope): applies for measurement of the airtightness of the building envelope. In this case, any intentional opening in the building envelope is closed or sealed.


